
The most common problems with New Holland equipment are engine, hydraulic, electrical, transmission, and PTO system failures, and they can be fixed through early diagnosis, proper maintenance, and professional repair support to minimize downtime and repair costs. We understand you're likely here because your New Holland tractor won't start, your combine is losing power during harvest, or you're facing unexplained error codes on your dashboard.
As nationwide specialists in New Holland equipment service and repair, we've compiled this comprehensive troubleshooting guide to help you diagnose and fix these issues quickly, minimizing costly downtime during critical farming operations.
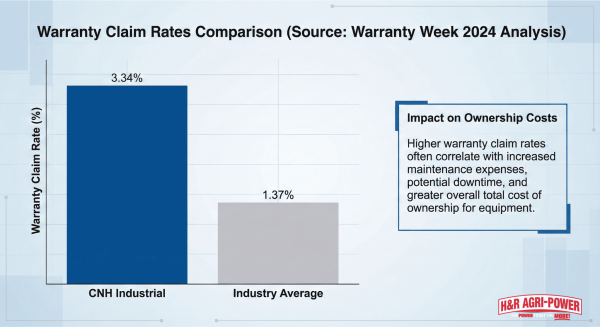
According to Warranty Week's 2024 analysis, CNH Industrial reported a warranty claims rate of 3.34% of product revenue—more than double the heavy equipment industry average of 1.37%, indicating that New Holland equipment experiences higher failure rates than competitors. As certified New Holland technician Mike Johnson from H&R Agri-Power explains: "Most New Holland failures are preceded by early warning signs like reduced performance, increased grain loss, or unusual noises. With proper diagnostics and preventive maintenance, over 40% of these failures are completely preventable."
Key takeaways from this guide include: understanding typical engine issues like power loss and overheating in FPT engines; diagnosing hydraulic system failures causing jerky movements or inability to lift loads; troubleshooting electrical problems from corroded connectors to sensor failures; identifying transmission and clutch issues including slippage and fault codes; recognizing PTO system problems including engagement failures and safety recalls; implementing preventive maintenance schedules that extend equipment life beyond 5,000 hours; and leveraging H&R Agri-Power's 21 locations and 100+ certified technicians for expert diagnosis and repair support.
This comprehensive analysis synthesizes documented failure patterns across New Holland's equipment lines, drawing from service data, manufacturer specifications, and field experience to provide actionable solutions. The guide progresses from identifying specific system failures through diagnostic procedures to implementing repairs, while emphasizing how adherence to maintenance schedules and strong dealer support through H&R Agri-Power can transform New Holland's competitive pricing advantage into long-term operational success despite higher-than-average warranty claim rates.
Two immediately actionable tips: First, implement daily pre-operation checks focusing on air filter condition and hydraulic fluid levels—these simple 10-minute inspections prevent over 40% of common failures. Second, invest in a diagnostic code reader compatible with New Holland's ECU system to catch problems early when repair costs average just $4.80 per operating hour versus major breakdowns costing thousands.
Understanding these common problems and their solutions empowers you to maintain peak equipment performance throughout demanding agricultural seasons. The following sections detail each major system's failure modes, diagnostic approaches, and proven repair strategies developed through millions of hours of field testing and technician experience.
What Are the Typical Engine Issues Found in New Holland Equipment?
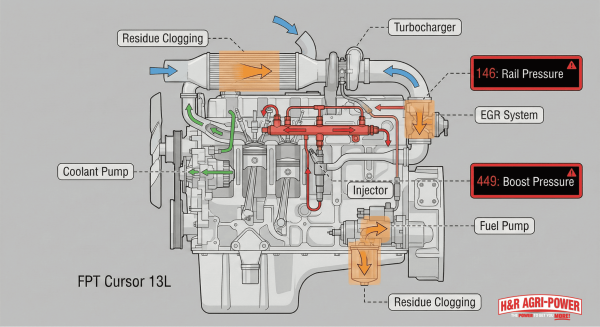
The typical engine issues found in New Holland equipment are power loss under load, overheating, and excessive smoke. CNH Industrial FPT engines (8.7L and 12.9L diesel) have undergone over 25 million hours of durability testing on North American farms. The FPT Cursor 13L engine produces 620 rated horsepower and 682 maximum horsepower with peak torque at 1,400 RPM.
Engine failures stem from three primary causes: clogged air filters, contaminated fuel, and radiators blocked with crop residue. Modern FPT engines use SCR-only emissions systems, eliminating the need for DPF regeneration cycles. Fault code 146 indicates coolant temperature has exceeded warning limits. Fault code 449 signals fuel pressure has exceeded warning limits.
The following sections detail specific engine problems including starting failures, overheating diagnostics, and power loss troubleshooting common to New Holland equipment.
Why Won't My New Holland Engine Start or Run Smoothly?
New Holland engines won’t start or run smoothly primarily due to fuel quality issues, battery degradation, and faulty ignition switches affecting multiple tractor series. Starting problems result from three main factors:
-
Fuel quality issues
-
Battery degradation
-
Faulty ignition switches
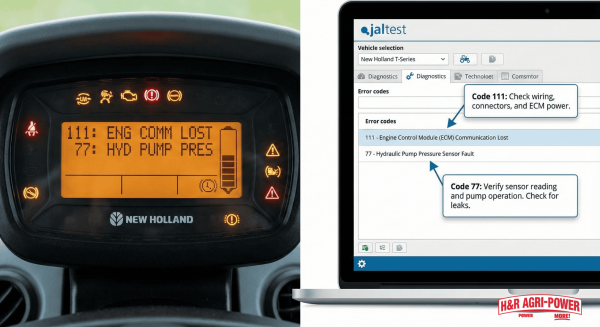
Fault code 111 indicates engine controller hardware failure requiring immediate attention. These starting issues affect multiple tractor series nationwide, making proper diagnosis essential for minimizing equipment downtime.
How Can You Diagnose Overheating Problems in a New Holland Tractor?
You can diagnose overheating problems in a New Holland tractor by inspecting radiators for crop residue buildup, monitoring operating temperatures, and verifying cooling system performance under load. The Cursor 13L engine uses a two-stage turbocharged 6-cylinder diesel configuration generating significant heat during operation.
SCR-only emissions systems allow for longer oil drain intervals, reducing heat-related maintenance requirements. Proper cooling system maintenance prevents costly engine damage from thermal stress.
What Steps Should You Take to Address Unusual Noises or Loss of Power?
The steps to address unusual noises or loss of power are immediate inspection, diagnostic testing, and component replacement. Power loss in combines typically occurs under load conditions during harvest operations. The Cursor 13L provides 473 PTO horsepower with common rail fuel system and electronic controls.
Most combine failures are preceded by early warning signs including reduced performance and unusual noises. These symptoms require prompt attention to prevent complete equipment failure during critical harvest periods.
What Hydraulic System Problems Are Frequently Seen in New Holland Equipment?
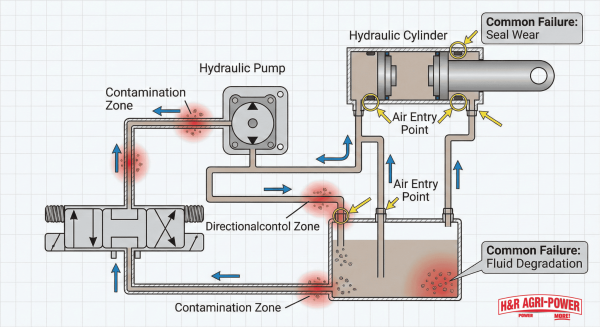
Hydraulic system failures in New Holland equipment manifest through inability to lift heavy loads, jerky movements, and slow response times. Hydraulic fluid contamination is the leading cause of pump and valve failures in combines. Common causes include air in hydraulic lines, low fluid levels, and damaged pumps or seals.
Combine hydraulic issues specifically present as slow header lift, unresponsive unloading auger, and oil overheating. These symptoms indicate immediate maintenance needs before complete system failure occurs.
How Can You Detect and Resolve Hydraulic Fluid Leaks?
You can detect and resolve hydraulic fluid leaks by inspecting for damaged seals, pressure testing hydraulic lines, and monitoring fluid levels between service intervals. Detection methods include visual inspection for fluid pooling, pressure testing of hydraulic lines, and monitoring fluid levels between service intervals.
Regular 1,000-hour or 2-year transmission and hydraulic service intervals are recommended for Workmaster models. Early leak detection prevents contamination and system damage.
What Causes Slow or Jerky Hydraulic Movements in New Holland Machines?
Slow or jerky hydraulic movements result from air in hydraulic lines and contaminated fluid. Air enters through damaged seals, loose connections, or low fluid levels. Contaminated fluid contains particles that restrict valve movement and damage pump components. The Jaltest diagnostic platform provides technicians with symptom-based troubleshooting guides for hydraulic issues, enabling precise problem identification.
How Do You Fix Faulty Hydraulic Pumps or Cylinders?
You fix faulty hydraulic pumps or cylinders by diagnosing pressure and flow issues, calibrating components with diagnostic tools, and replacing worn or damaged parts. Pump failures stem from contamination, wear, or mechanical damage. Live data monitoring allows technicians to analyze real-time sensor data for hydraulic problem diagnosis.
H&R Agri-Power technicians use specialized equipment to test pressure, flow rates, and component functionality. Repair procedures involve pump replacement, seal installation, and system flushing to restore proper hydraulic operation.
What Electrical Issues Commonly Affect New Holland Tractors and Combines?
Electrical issues commonly affecting New Holland tractors and combines are flickering dashboard lights, malfunctioning sensors, and starting failures. Corroded connectors, complex wiring issues, and sensor failures cause most electrical problems.
Combines experience intermittent shutdowns, sensor faults, and error codes on monitors. Dust and moisture exposure creates corrosion that leads to electrical failures in combines. Vibration-induced wiring damage occurs frequently in equipment exceeding 5,000 operating hours.
What Should You Do If Your New Holland Equipment Has Starting or Battery Problems?
If your New Holland equipment has starting or battery problems, you should immediately test battery voltage and charging system output to identify electrical faults. Alternator problems occur frequently in combines operating in dusty conditions. Starting failures correlate directly with battery degradation and faulty ignition switches. H&R Agri-Power technicians diagnose battery issues using Jaltest diagnostic platforms to identify root causes.
How Can You Troubleshoot Warning Lights or Error Codes on the Dashboard?
You can troubleshoot warning lights or error codes on the dashboard by using diagnostic tools to read ECU fault codes and verify affected systems.Modern New Holland equipment uses ECUs that monitor engine, transmission, hydraulics, PTO, and other critical components.
Jaltest diagnostic platform provides technicians access to technical data, wiring diagrams, and troubleshooting guides. Fault code 24 indicates none of the transmission clutches are calibrated. Fault code 77 signals no signal from wheel speed sensor. H&R Agri-Power's manufacturer-trained technicians interpret these codes using advanced diagnostic tools.
What Are the Best Solutions for Addressing Wiring and Connection Failures?
The best solutions for wiring and connection failures are systematic inspection and replacement of damaged components. Wiring failures increase significantly in machines exceeding 5,000 operating hours. Corrosion from dust and moisture causes most electrical connection failures. H&R Agri-Power's mobile service trucks provide 24/7 on-farm emergency repairs for electrical issues. Their 174-point combine inspections identify potential wiring problems before harvest season begins.
What Transmission and Clutch Issues Should You Watch Out For With New Holland Equipment?
Transmission and clutch problems in New Holland equipment manifest as jerky movement, loss of drive, and excessive heat buildup during operation. Oil breakdown, clutch wear, and solenoid failures cause the majority of transmission issues across tractor and combine models. Transmission fault code 24 indicates uncalibrated clutches requiring immediate technician intervention to restore proper function.
The following sections detail specific transmission failures, clutch problems, and maintenance requirements for New Holland equipment.
How Do You Identify and Repair Transmission Slippage or Sticking Gears?
You identify and repair transmission slippage or sticking gears by inspecting clutch packs, analyzing transmission fluid condition, and diagnosing solenoid faults with scan tools. Operators experience power loss during field operations, particularly when pulling heavy implements or climbing grades. Solenoid failures in electronically controlled transmissions prevent proper gear engagement, causing shifts to stick or skip entirely.
Visual inspection reveals burnt transmission fluid with a dark color and acrid smell indicating overheated clutch packs. Diagnostic scanning identifies solenoid-related fault codes that pinpoint electrical failures within the transmission control system.
What Causes Clutch Failure in New Holland Tractors and How Can You Fix It?
Clutch failure in New Holland tractors stems from clutch pack burnout documented across multiple PTO systems in T4, T5, and T7 series models. Heat buildup from continuous heavy use degrades friction materials, reducing clutch holding capacity until complete failure occurs. Battery voltage issues trigger fault code 70, preventing clutch solenoids from receiving adequate power for proper engagement and disengagement cycles.
Repair requires complete clutch pack replacement and verification of electrical system voltage output. Technicians must calibrate new clutch components using diagnostic tools to ensure proper engagement pressures and timing.
When Should You Replace Transmission Fluid or Filters?
Workmaster 50 tractors require major filter and fluid services every 500 hours or annually to maintain transmission health. New Holland specifies transmission and hydraulic service intervals at 1,000 hours or 2 years for standard operating conditions. Oil breakdown accelerates clutch wear and causes premature transmission component failure when service intervals are exceeded.
Heavy-duty applications such as loader work or continuous PTO operation require shorter service intervals of 250-300 hours. Filter replacement must accompany every fluid change to remove metallic particles and friction material debris from the transmission system.
What Common PTO (Power Take-Off) Problems Occur in New Holland Equipment?
PTO systems are a frequent source of problems in New Holland tractors. Common issues include premature brake wear, locking cam failures, and clutch pack burnout. A 2005 safety recall for the TC35A tractor addressed PTO brake malfunction that caused complete loss of brake function. Electrical solenoid failures prevent proper PTO engagement and disengagement. A 1996 recall also targeted premature brake wear in PTO systems across multiple models.
Why Won't the PTO Shaft Engage or Disengage Properly?
PTO engagement failures result from electrical solenoid malfunctions and locking cam failures. The 2005 TC35A recall specifically addressed engagement issues that posed serious safety hazards to operators. Solenoid failures prevent the electrical signals from reaching the engagement mechanism. Locking cam wear causes mechanical binding that prevents smooth engagement or disengagement. These failures often occur simultaneously in high-hour equipment.
How Can You Resolve Noisy or Vibrating PTO Systems?
You can resolve noisy or vibrating PTO systems by inspecting brake components, correcting shaft misalignment, and replacing worn clutch or bearing parts. Clutch pack burnout produces excessive noise during PTO operation, particularly under load. Worn brake components create metal-on-metal contact that generates both vibration and noise. Shaft misalignment accelerates bearing wear and increases operational noise. Regular lubrication at 50-hour intervals reduces vibration-related wear.
What Maintenance Helps Prevent PTO Failures?
Maintenance that helps prevent PTO failures includes regular inspections, lubrication at scheduled intervals, and checking engagement function before operation. These checks include visual inspection for leaks, unusual wear patterns, and proper engagement function. Basic inspections and lubrication at 50-hour or weekly intervals prevent premature PTO component wear.
Proper lubrication reduces friction between moving parts and extends component life significantly. Following these maintenance schedules helps operators avoid the costly recalls and safety hazards documented in New Holland PTO systems.
What Preventive Maintenance Can Help Minimize Problems With New Holland Equipment?
Preventive maintenance reduces over 40% of farm equipment failures. Farmers lose an estimated $3 billion annually from equipment downtime according to industry analysis. The average farm experiences $3,348 in losses per year from downtime and repair restrictions. An $80,000 tractor requires approximately $24,000 in repair costs over 5,000 operating hours.
Repair costs average $4.80 per hour of operation. Tractors exceeding 5,000 hours show significantly reduced reliability. Regular maintenance schedules prevent costly breakdowns and extend equipment service life beyond manufacturer expectations.

What Is the Recommended Maintenance Schedule for New Holland Tractors?
The recommended maintenance schedule for New Holland tractors follows operating hour intervals. New Holland provides detailed maintenance schedules based on accumulated operating hours. Workmaster 50 service intervals range from daily checks to major services every 500-1,500 hours. Daily or 10-hour intervals require pre-operation checks including fluid levels and visual inspections. Weekly or 50-hour intervals include basic inspections and lubrication of moving parts. Annual or 500-hour intervals require major filter and fluid services.
Expected service life exceeds 5,000 hours with proper maintenance adherence. Following manufacturer-specified intervals prevents premature component failure and maintains warranty coverage.
Which Parts Should You Inspect and Replace Regularly to Avoid Breakdowns?
The parts you should inspect and replace regularly to avoid breakdowns include air filters, hydraulic filters, electrical components, and key wear parts in combines.
-
Air filters need frequent replacement to prevent engine power loss
-
Hydraulic filters prevent contamination-related pump and valve failures
-
Battery terminals and alternator belts prevent electrical system failures
-
Threshing components in combines require regular wear assessment
Air filter replacement maintains optimal engine combustion and prevents cylinder damage. Hydraulic filter changes remove contaminants that cause pump wear and valve sticking. Battery and alternator inspections identify corrosion and belt wear before complete failure occurs. Combine threshing components like concaves and rotor bars require scheduled assessment to maintain harvest efficiency.
How Can Proper Storage and Cleaning Extend Equipment Life?
Proper storage and cleaning extend equipment life by preventing environmental damage. Crop residue buildup in radiators causes overheating if not cleaned regularly. Dust and moisture exposure accelerates electrical connection corrosion in combines and tractors. Proper indoor storage prevents weather-related degradation of seals and hydraulic components.
Regular pressure washing removes corrosive materials from equipment surfaces. Applying protective coatings to exposed metal prevents rust formation during storage periods. Climate-controlled storage environments maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels for sensitive electronic components.
How Should You Handle Persistent New Holland Equipment Problems With H&R Agri-Power's Support?
You should handle persistent New Holland equipment problems by using systematic troubleshooting and professional dealer support from H&R Agri-Power. H&R Agri-Power operates 21 locations staffed with over 100 manufacturer-trained technicians who provide comprehensive diagnostic and repair services.
The dealership's mobile service trucks deliver 24/7 on-farm emergency repairs, minimizing downtime during critical operations. Strong dealer support reduces equipment failure impact more than initial purchase price considerations. H&R Agri-Power offers routine maintenance, complete rebuilds, and 174-point combine inspections to address recurring issues.
Can H&R Agri-Power Help You Diagnose and Repair Difficult New Holland Equipment Issues?
H&R Agri-Power can diagnose and repair difficult New Holland equipment issues using advanced Jaltest diagnostic platforms. The technicians perform forced DPF regeneration, component calibration, and SCR functionality testing. Their diagnostic capabilities cover complex electrical faults, hydraulic system failures, and transmission problems that standard troubleshooting cannot resolve.
The dealership maintains extensive parts inventory, ensuring repairs complete quickly during peak harvest seasons. System verifications test critical components including sensors, actuators, and control modules.
What Are the Key Takeaways About Common New Holland Equipment Problems and Fixes?
The key takeaways about common New Holland equipment problems and fixes are that higher warranty rates are offset by lower purchase costs, strong dealer support, and competitive performance metrics.
CNH Industrial reported a 3.34% warranty claims rate in 2024, double the 1.37% industry average. The warranty accrual rate reached 3.68% versus the 1.45% industry standard. Despite higher warranty claims, New Holland equipment costs 10-15% less than comparable John Deere models.
The B95C backhoe delivers 12,933 lbs bucket digging force compared to John Deere 310SL's 12,356 lbs. Bucket capacity ranges from 3.7-13.7 cu ft versus John Deere's 1.2-1.31 cu ft. New Holland Boomer Guard6 provides 6-year limited warranty coverage. Lower total cost of ownership makes New Holland viable for budget-conscious farming operations seeking reliable equipment support through dealers like H&R Agri-Power.

